Understanding Dual Diagnosis: Everything You Need to Know
What is Dual Diagnosis
In the realm of mental health and addiction, the term “dual diagnosis” has gained increasing significance. Understanding dual diagnosis is essential for both professionals in the field and those affected.
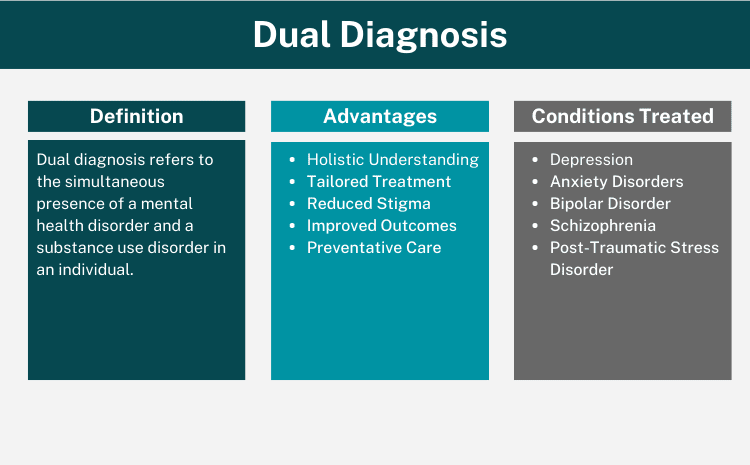
In its simplest form, dual diagnosis refers to the simultaneous presence of a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder in an individual. It’s essential to note that while the term “dual diagnosis” may sound like a specific condition, it isn’t a singular diagnosis. Instead, it represents a combination of diagnoses.
Mental health disorders can encompass a range of conditions, including depression, anxiety, and other related ailments. On the flip side, a substance use disorder can involve an addiction to alcohol, drugs, or other potentially harmful substances. The crux of understanding dual diagnosis lies in recognizing the interplay between these disorders.
When co-existing, each condition can amplify the effects of the other. For instance, untreated mental health challenges can exacerbate substance use issues, leading to increased consumption. Conversely, heightened substance use can further deteriorate one’s mental well-being, setting off a damaging cyclical pattern.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we’ll explore the complexities and nuances associated with dual diagnosis, shedding light on its implications and the paths toward recovery.
Dual Diagnosis vs. Co-Occurring Disorders: Is There a Difference?
In the realm of mental health and addiction, terminologies can sometimes overlap, leading to potential confusion. Let’s demystify this. The term “dual diagnosis” refers to an individual grappling with both a mental disorder and a substance abuse disorder. On the other hand, “co-occurring disorder” — a more recent term — essentially carries the same meaning.
However, it’s worth noting that co-occurring disorders can also encompass combinations like mental disorders paired with intellectual disabilities. While both terms often address the intersection of mental illness and substance use, ‘co-occurring disorders’ can be a broader term, including other dual challenges an individual might face.
The Interplay Between Substance Abuse and Mental Health
The intricate relationship between substance abuse and mental health has long been a subject of research and discussion. Recent studies shed light on this connection, revealing that half of the individuals who encounter a substance use disorder during their lives will also grapple with a mental health disorder, and vice versa.
To put this into perspective, in 2020 alone, a staggering 17 million U.S. adults found themselves battling both a mental health disorder and a substance use disorder. Such statistics underline the intertwined nature of addiction and mental health, emphasizing the need for comprehensive understanding and care.
Triggers and Impacts: Which Comes First?
The interwoven relationship between mental health and substance abuse often leaves one pondering: which comes first? To shed light on this, let’s delve into some of the primary triggers that often lead individuals down the path of substance abuse and mental health challenges:
- Stress: Often, individuals resort to substance use as a coping mechanism for stress, unknowingly setting the stage for potential addiction.
- Traumatic Events: Experiencing trauma can lead to mental health issues. Individuals might turn to drugs or alcohol to numb the pain or escape reality.
- Peer Pressure: The environment and company one keep can influence substance use, potentially leading to addiction and subsequent mental health challenges.
- Genetic Predisposition: Genetics can play a role where an individual might be predisposed to both mental illness and substance abuse.
- Chemical Imbalances: Using substances can alter brain chemistry, which can exacerbate or even trigger mental health issues.
Understanding these triggers offers invaluable insights into the cause-and-effect dynamics of mental disorders and substance abuse, paving the way for more effective interventions and treatments.
Recognizing and Diagnosing Dual Disorders
Curiously, while the effects and challenges of dual diagnoses are evident, there’s no specific diagnostic criterion for it in the DSM-IV-TR. However, understanding the symptoms can be a pivotal step in seeking help and intervention for oneself or a loved one.
Key Symptoms of Co-Occurring Disorders
Recognizing the specific symptoms of co-occurring disorders can be challenging due to their overlapping nature. However, for clarity, let’s break down the symptoms associated with substance use disorders and mental health disorders:
Substance Use Disorder Symptoms:
- Distancing from Social Circles: A noticeable distance or withdrawal from family and friends.
- Problems Focussing: Difficulty maintaining focus or staying on task.
- Behavioral Changes: Sudden, inexplicable changes in behavior.
- Risky Behaviors: Engaging in risky behaviors, especially when under the influence.
- Tolerance & Withdrawal: Developing a heightened tolerance to alcohol or drugs, leading to increased intake, and experiencing withdrawal symptoms in its absence.
- Dependency: A growing sense that one needs the substance to function or to cope with daily life.
Mental Health Disorder Symptoms:
- Mood Changes: Extreme mood changes, swinging from highs to lows, often evident in conditions like bipolar disorder.
- Cognitive Disarray: Confusion or feeling out of touch with reality.
- Concentration Problems: Problems focusing or concentrating on tasks.
- Functionality Issues: Struggles with daily tasks, including challenges at work or school.
- Social Avoidance: A tendency to avoid social activities or events, possibly due to anxiety, depression, or mental health problem.
- Suicidal Thoughts: Harboring thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
The Diagnostic Journey
Diagnosis a Dual Diagnosis requires a systematic approach to ensure accurate diagnosis, especially given the overlapping nature of symptoms. Here’s a glimpse into the multifaceted diagnostic journey:
- Clinical History: An in-depth interview helps professionals gather a thorough history of the patient, detailing past incidents, patterns, and existing symptoms.
- Physical Examination: While mental disorders are primarily psychological, a physical exam can rule out other medical conditions that might mimic psychiatric symptoms.
- Investigative Procedures: Diagnostic tests, including blood and urine tests or even scans, assist in identifying substance use disorders or potential underlying causes like thyroid issues that could manifest as psychiatric symptoms.
- Differential Diagnosis: This step involves evaluating a patient’s complaints and symptoms, contrasting them with known conditions, including disorders like schizophrenia.
- Diagnostic Evaluation: This encompasses designing a structured diagnostic plan, keeping in mind the nuances of dual disorders, to ascertain the most accurate diagnosis possible.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies
Navigating the complexities of dual diagnosis necessitates a multifaceted approach to treatment. Leveraging a combination of therapies and interventions ensures a holistic path to dual diagnosis recovery.
Behavioral Therapy and Its Role
Behavioral therapy plays a pivotal role in addressing the intricacies of dual disorders. It provides tools and strategies that enable individuals to reshape their thought patterns and behaviors, directly influencing their recovery journey. Two prominent therapies include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This modality teaches individuals to identify and transform ineffective thought patterns, promoting healthier behaviors and responses.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): Especially effective for those exhibiting self-harm behaviors like drug use or self-injury, DBT equips individuals with coping mechanisms and strategies to regulate emotions.
Medication Management in Dual Diagnosis
While therapy lays the groundwork for understanding and managing dual disorders, medication often plays an integral role in the treatment plan. Medications can help to alleviate symptoms associated with both mental health disorders and substance use disorders.
The Importance of Support Groups
Going through dual diagnosis recovery isn’t something you do alone. Having a support network makes a big difference. Joining support groups gives you a chance to connect with people who’ve faced the same challenges. They offer advice, share their stories, and help you feel understood. Outside of these groups, your friends, family, and community are vital too. They provide the encouragement and safe space you need while you work through the ups and downs of dual diagnosis
How to Support Someone with Dual Diagnosis
When someone you care about is on their dual diagnosis recovery journey, you might feel a mix of emotions and uncertainties. Here’s some guidance on how to be there for them:
- Educate Yourself: Understand what dual diagnosis means. The better informed you are about addiction and mental health challenges, the more empathetic and effective your support will be.
- Be Patient: Recovery isn’t linear; there will be good days and tough ones. Offer your patience as they navigate the ups and downs.
- Avoid Judgment: Reinforce that their dual diagnosis doesn’t define them. Avoid passing judgments or using stigmatizing language.
- Encourage Treatment: Gently remind them of the importance of sticking with their treatment plans, attending therapy sessions, and taking prescribed medications.
- Listen Actively: Sometimes, they might just need someone to listen. Offer a listening ear without rushing to give advice.
- Join Support Groups: Consider attending family therapy or support groups designed for loved ones of individuals with dual diagnosis. This can provide you with tools and coping mechanisms.
- Set Boundaries: While being supportive is vital, it’s also essential to establish and maintain personal boundaries to ensure your well-being.
Remember, supporting someone with a dual diagnosis is a journey in itself. While it’s crucial to be there for them, don’t forget to also take care of your own mental and emotional health.
Minimizing the Risks of Suffering a Dual Diagnosis
Understanding and addressing the factors that lead to dual diagnosis is crucial. By actively focusing on prevention and early intervention, individuals can reduce the risks associated with this condition. Here are some steps to consider:
- Stay Informed: Knowledge is power. Familiarize yourself with the signs and symptoms of both mental health issues and substance use disorders. This can help in early detection and intervention.
- Seek Early Treatment: If you or someone you know starts exhibiting signs of a mental health condition or substance misuse, seek advice from a health professional or a dual diagnosis treatment center promptly.
- Limit Substance Exposure: Limit or avoid the use of substances, especially if there’s a history of mental health issues in your family. Remember, substance use can exacerbate underlying mental health conditions.
- Prioritize Mental Well-being: Engage in activities that promote mental wellness, such as regular exercise, meditation, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle.
- Stay Connected: Building and maintaining strong social connections can act as a buffer against mental health challenges and substance misuse. Engage in community activities, join support groups, and nurture personal relationships.
Seek Help for Dual Diagnosis: Your Health Matters
Navigating the complexities of dual diagnosis can be daunting.Understanding the intertwined nature of mental health issues and substance use offers a beacon of hope. Early recognition and targeted treatment are crucial for breaking the cycle.
With available support networks, behavioral therapies, and medication, recovery is within reach. The first step, often the most significant, is reaching out for assistance. If you or someone you love might be grappling with a dual diagnosis, don’t delay. Embracing both mental and physical well-being is paramount, and with the right help, a healthier and brighter future is attainable. Understanding dual challenges is the initial step in facing them with confidence.
The financial aspect of IOPs is a significant concern for many. It’s crucial to understand the costs involved, insurance considerations, and potential financial aid or payment plans that might be available.
